Wireless
Q: Are IoTize wireless products qualified for my market / industry?
IoTize obtains CE (CE-RED), FCC and IC qualification of all its wireless products that require them. Documentation of these qualifications is included on our product pages and in our product datasheets.
For any qualification that you may require for your product, you benefit from the availability of the test results and qualifications that IoTize obtains for our wireless products.
If you require qualification of an IoTize wireless product for a specific market or industry, email us using our contact form.
Q: Does IoTize provide antenna recommendations or design support?
A key advantage to our solutions is that you don't have to do any wireless design. IoTize products include embedded antennas for any channels (NFC, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, etc.) that are available on the wireless module. The embedded antennas are tested and optimized for interoperability. Qualification testing includes testing of the complete wireless implementation including the antenna.
Refer to the product datasheets for wireless characteristics.
If you require a specific antenna, email us using our contact form.
Q: What is NFC connectivity?
NFC stands for Near Field Communication. It is a very-short range or "proximity" wireless technology. It communicates over a distance of 2 to 4 centimeters (0.75 to 1.5 inches). NFC is an evolution of contactless 13.56 Mhz Radio Frequency ID technologies (RFID). In fact, NFC regroups several 13.56 Mhz wireless standards (ISO-14443, ISO-15693, FeliCa, etc.) under a common standard that is managed and promoted by a non-profit association called the NFC Forum. NFC is increasingly found on mobile devices. NFC makes it possible for mobiles to be used like contactless smart cards (ex. for payment or transportation applications) or as contactless card / tag readers.
Read more about IoTize's use of NFC.
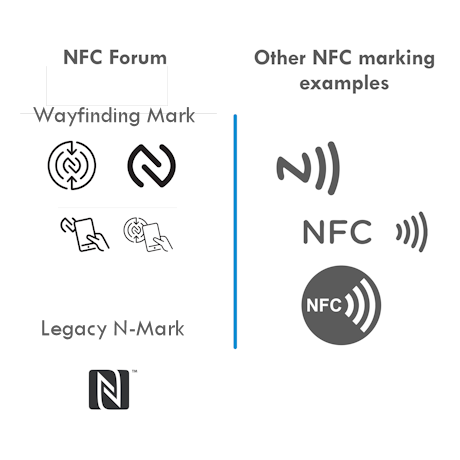
Q: How do I know if an appliance or system has NFC connectivity?
The best way to know if a mobile device has Near Field Communication is to check the manufacturer's specification.
However, even if you know an appliance has NFC, it is also important to know where the NFC interface is located, because the range of the wireless signal is only about 3 centimeters (1 inch). The common marking to indicate the location of an NFC interface is the N-mark (recommended for use in NFC qualified devices by NFC Forum).
Note that some manufacturers choose to use a marking of their own design to indicate where the NFC interface is located. In some cases, may have to verify in the appliance's documentation or with the manufacturer.
More about IoTize's use of NFC.
Q: How do I know what mobiles have NFC?
The best way to know if a mobile device has Near Field Communication is to check the manufacturer's specification.
Note that the trend and usage of NFC on mobiles is different from one OS to another:
- Android: NFC is present and fully implemented on the large majority of mobiles.
- iOS: NFC is present on iPhone since its introduction for Apple Pay applications in 2015. However it is only since the release of iOS-13 that Apple has enabled the full range of NFC features that will enable things like NFC-enhanced Bluetooth pairing.
More about IoTize's use of NFC.
Q: What is Bluetooth pairing?
To set up a wireless point-to-point connection between a Bluetooth-equiped mobile and another applinace or device, you must follow a process of selection and authentication. This is called pairing. It involves:
- Making the mobile 'discoverable'
- Starting the Bluetooth connection of the other appliance
- Selecting the applinace from a list of Bluetooth devices on the mobile
- Entering the correct, 4-digit identifier for the applinace (you may have to check its documentation to find this).
The automation of this process using Near Field Communication (NFC) is increasingly common on Bluetooth equipped appliances. If NFC is implemented on the Bluetooth appliance, pairing an NFC equipped-mobile with it is as simple as approaching the mobile to with in 3 centimeters of the NFC tag on the device.
Read more about NFC-enhanced Bluetooth pairing.
Q: What is NFC 3-stroke configuration ?
3-stroke configuration is a technology use case for NFC. NFC enables point to point wireless communication over a very short range of a few centimeters. However, for frequent configurations of a system or appliance, a mobile with NFC can be used in 3 simple and intuitive steps to:
- recuperate the actual configuration of the appliance
- change the configuration on the mobile
- transmit the new configuration to the appliance
NFC has the advantages of being a very simple, inexpensive and a secure technology for this type of implementation when compared to other wireless technologies.
Read more about NFC 3-Stroke Configuration.
Q: Is NFC a secure wireless technology?
NFC, or Near Field Communication, is derived from technologies and standards that were originally used in applications such as payments (credit, debit cards) and identity (passports, drivers licenses, etc.). NFC has several security advantages compared to other, longer-range wireless technologies including:
- Passive NFC devices (tags or cards) don't draw unwanted attention by emitting a permanent advertising signal. Only the mobile will emit its carrier signal, and this can be switched off and on at will.
- NFC can be used to automate pairing and encryption key exchanges reducing this process to a fraction of a second and eliminating the need to manually select a device to connect to and enter pairing codes or keys.
- NFC's short range of only a few centimeters reduces the risks of someone else intercepting the signal and thus reduces risks of Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacks.
For these reasons NFC is often considered an excellent complement to technologies like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi when connecting mobile devices for point-to-point communication with other systems or appliances.
Read more about NFC security advantages.



